- Membrane bound organelles, eukaryotic
- Membrane lipids have ester bonds
- Represented by the four kingdoms
- Nervous system present in kingdom animalia
Organism 1: House dog
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Suborder: Caniformia
Family: Canidae
Genus: Canis
Species: C. lupus
Subspecies: C. lupus. familiaris
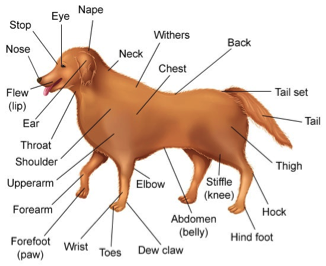
Figure 12: Dog Diagram
Figure 13: Golden Retriever Puppy
The dog is a multicellular organism. The species is almost always bread under captivity, and is a common pet among families. There is a large range in possible sizes, as some dogs can be as little as only a couple inches tall and weigh only several pounds. Other dogs can grow as large as 30 to 40 inches in height and weigh over 200 pounds [19]. Dogs are one of the most common American pet, as many breeds are typically very friendly to humans. It is rare to find these animals in the wild, as they are a domesticated species. There are many different breeds which are native to countries all across the world [19].
Why does it belong?
The Canis lupus familiaris, often simply referred to as a house dog is a Eukaryote becauseit has membrane bound organelles in its cells.
Organism 2: Beach rose
Kingdom: Plantae
Phylum: Spermatophyta
Class: Magnoliopsida
Order: Rosales
Genus: Rosa
Species: Rosa rugosa

Figure 14: Rosa rugosa

Figure 15: Rosa rugosa labeled diagram
The Rosa rugosa is native to Japan, Korea, and China. It grows 4 to 6 feet tall and has a rounded shape. The leaflets have a wrinkled look to them, which is where it gets the name rugosa. The fragrant flowers range in color from white to rose pink. The flower part is 3 and a quarter inches across. The Rosa rugosa is famous for its excellent resistance to disease. Most roses are very susceptible to disease but the Rosa rugosa is the exact opposite. They are used in gardens as a fence using their thorns [20]. They are also used to keep sand or dunes from eroding [21]. The leaves conserve water very well with their waxy, thick texture. This is important to the flower because it is native to very sandy, dry areas, especially those in Asia [22].
Why does it belong?
The Rosa rugosa has membrane bound organelles, which makes it a part of the Domain Eukarya. This is compared to archaea and bacteria, which do not have membrane bound organelles.